Square Column with Spiral Reinforcement
Spiral Spacing Calculation for Square Section – C20-S420
Example Problem
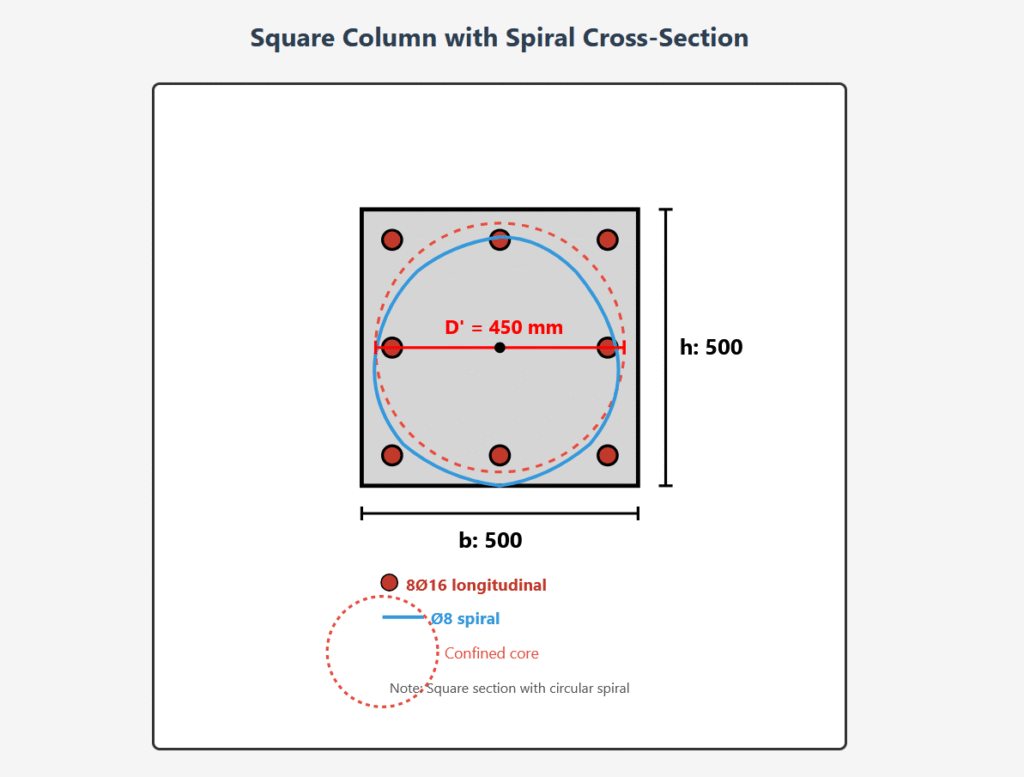
For a square column with C20-S420 materials shown in the figure, calculate the required spiral spacing using Ø8 spiral reinforcement. The column will carry the axial load that corresponds to its given longitudinal reinforcement.
Given: 8Ø16 longitudinal bars, Ø8 spiral
Square Column with Spiral Cross-Section
Given Information
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Column section | Square 500 × 500 mm |
| Spiral core diameter | D’ = 450 mm (inscribed circle) |
| Materials | C20-S420 (fcd = 13 MPa, fyd = 365 MPa, fck = 20 MPa, fywk = 365 MPa) |
| Longitudinal reinforcement | 8Ø16 (given) |
| Spiral bar diameter | Ø8 mm |
SOLUTION
Calculate Longitudinal Steel Area
Ast = 8 × 201 = 1,608 mm²
Calculate Column Areas
Ac = b × h = 500² = 250,000 mm²
Core area (circular spiral):
Ack = π D’²/4 = π × 450²/4 = 158,963 mm²
Calculate Column Axial Capacity
Nd = (0.85 × 13 × 250,000) + (365 × 1,608)
Nd = 2,762,500 + 586,920
Nd = 3,349,420 N ≈ 3,349.42 kN
This calculates the axial load capacity of the column based on the given 8Ø16 longitudinal reinforcement. This capacity will be used to determine if spiral reinforcement is required.
Check if Spiral is Required
3,349.42 × 10³ > 0.20 × 250,000 × 20
3,349,420 > 1,000,000 N
3,349.42 × 10³ > 1,000 × 10³ ✓
Calculate Required Volumetric Spiral Ratio
Two Conditions (Select Larger):
ρst ≥ 0.45 [(Ac/Ack) – 1] × (fck/fywk)
Condition 2:
ρst ≥ 0.12 × (fck/fywk)
Calculate Condition 1:
ρst ≥ 0.45 × [1.573 – 1] × 0.0548
ρst ≥ 0.45 × 0.573 × 0.0548
ρst ≥ 0.014
Calculate Condition 2:
ρst ≥ 0.12 × 0.0548
ρst ≥ 0.00657
Calculate Required Spiral Steel Area per Unit Height
Ast = 0.014 × 158,963
Ast = 2,225.5 mm²
This represents the required spiral cross-sectional area per millimeter of column height. This value will be used to determine the spiral pitch (vertical spacing).
Calculate Spiral Spacing from Requirements
Where:
D = core diameter = 450 mm
Aswt = area of spiral bar = π × 8²/4 = 50.24 mm²
Ast = 2,225.5 mm²
st = (3.14 × 450 × 50.24) / 2,225.5
st = 70,989.6 / 2,225.5
st = 31.89 mm → Round to 40 mm
Apply Code Maximum Spacing Limits
Maximum Spacing Requirements:
D/5 = 450/5 = 90 mm
80 mm
}
Therefore: st ≤ 80 mm
Our calculated spacing (40 mm) is well below the maximum allowed (80 mm), so it controls the design.
Design Summary
Final Column Design – Side View
| Parameter | Value | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Column section | 500 × 500 mm (square) | Given |
| Gross area (Ac) | 250,000 mm² | Calculated |
| Core diameter (D’) | 450 mm | Given |
| Core area (Ack) | 158,963 mm² | Circular area |
| Longitudinal steel | 8Ø16 = 1,608 mm² | Given |
| Column capacity (Nd) | 3,349.42 kN | Calculated |
| Spiral requirement check | 3,349.42 kN > 1,000 kN | ✓ Spiral required |
| Volumetric ratio (ρst) | 0.014 | Larger of two conditions |
| Required steel per unit height | 2,225.5 mm² | Calculated |
| Calculated spacing | 31.89 mm → 40 mm | Rounded up |
| Maximum allowed spacing | 80 mm | Code limit (min of D/5, 80mm) |
| Final spiral design | Ø8 / 40 mm | ✓ Controls design |
Key Design Insights
- Unique configuration: This is a square column section with circular spiral reinforcement – an uncommon but valid design approach combining benefits of both systems.
- Core area calculation: Even though the column is square (500×500), the spiral creates a circular confined core with diameter 450mm, giving Ack = 158,963 mm².
- High axial capacity: With Nd = 3,349 kN >> 0.20Acfck = 1,000 kN, the column is heavily loaded and clearly requires spiral reinforcement.
- Condition 1 governs: The volumetric ratio from Condition 1 (0.014) is larger than Condition 2 (0.00657), so it controls the design.
- Tight spiral spacing: The calculated 40mm spacing is quite tight, providing excellent confinement but requiring careful construction.
- Well below limits: Design spacing (40mm) is well below the maximum code limit (80mm), indicating conservative and safe design.
- Corners unconfined: Note that the square corners outside the circular spiral are not confined – this must be considered in seismic design.
Advantages and Considerations
Advantages:
- Excellent confinement within the circular core
- Continuous spiral (no weak zones)
- Good ductility and toughness
- Square section easier to form and connect to beams
Design Considerations:
- Corner regions outside spiral are unconfined
- May require additional corner reinforcement in seismic zones
- More complex construction than pure square or circular columns
- Tight spiral spacing (40mm) requires careful workmanship
Final Construction Specifications
COLUMN: 500 × 500 mm (Square Section)
Spiral Core Diameter: 450 mm
Longitudinal Reinforcement: 8Ø16
(8 bars of 16mm diameter)
Spiral Reinforcement: Ø8 @ 40 mm pitch
(Continuous circular spiral, 8mm diameter, 40mm vertical spacing)
Materials: C20 Concrete, S420 Steel
Axial Capacity: Nd = 3,349 kN
- Spiral continuity: Ensure spiral is continuous or properly lap-spliced (minimum 48db)
- Tight spacing: 40mm spacing is tight – use proper spacers to maintain uniform pitch
- Longitudinal bar placement: 8 bars should be positioned around the perimeter, with at least one bar in each corner plus mid-face positions
- Corner confinement: Consider additional measures for corner regions in seismic applications
- Spiral anchorage: Provide 1.5 extra spiral turns at top and bottom with proper anchorage
- Concrete placement: Tight spiral may make concrete placement challenging – use appropriate consolidation methods
- Quality control: Verify spiral spacing during construction – tolerance should not exceed ±5mm
- Professional review: All designs must be reviewed by a licensed structural engineer