RC Column Design: Longitudinal & Shear Reinforcement
Step-by-Step Solution with Tie Spacing Calculation
Problem Statement
Design a reinforced concrete rectangular column for a multi-story commercial building. The column must resist both axial load and minimum moment conditions. Calculate:
1. Longitudinal steel reinforcement (main bars)
2. Transverse reinforcement (ties/stirrups) for shear
Material Properties
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete Class | C25 | fck = 25 MPa |
| Steel Class | S420 | fyk = 420 MPa |
| fcd | 16.67 MPa | Design concrete strength (25/1.5) |
| fyd | 365 MPa | Design steel strength (420/1.15) |
| Cover | d’ = 25 mm | Concrete cover to main reinforcement |
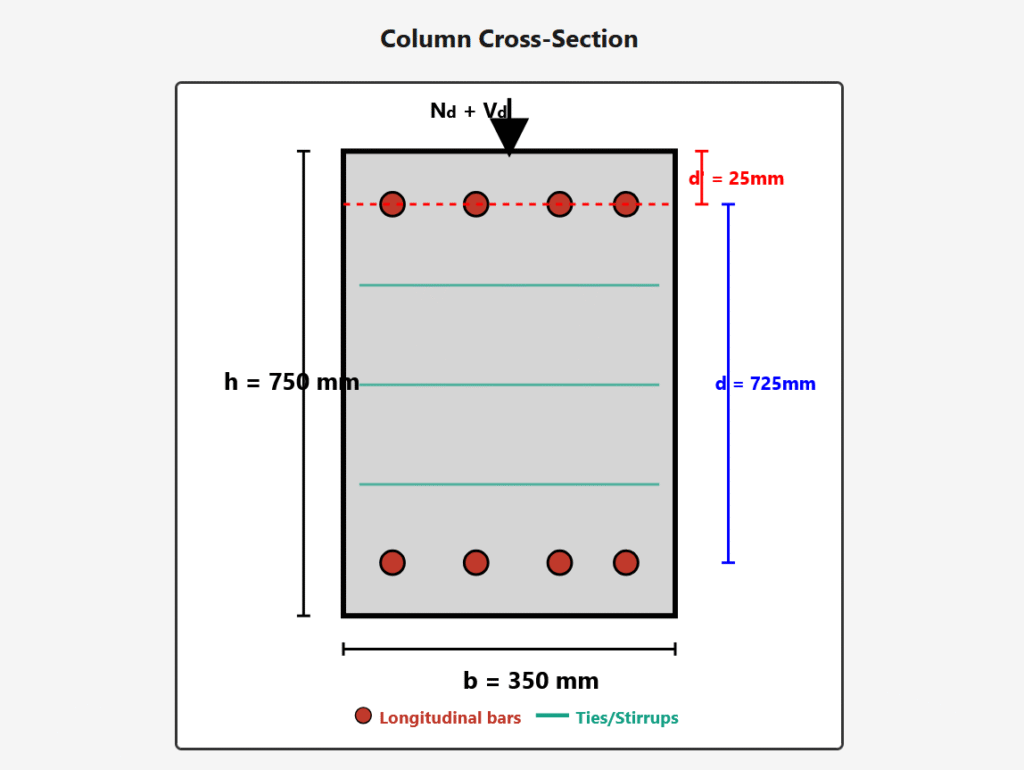
Column Geometry and Loading
Column Cross-Section
- Width (b): 350 mm
- Height (h): 750 mm
- Cover (d’): 25 mm
- Effective depth (d): 750 – 25 = 725 mm
- Reinforcement: 8 longitudinal bars + transverse ties
Design Loading
| Load Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Axial Force (Nd) | 1150 kN |
| Minimum Moment Condition | emin = 15 + 0.03h |
| Shear Force (Vd) | 185 kN |
PART 1: LONGITUDINAL REINFORCEMENT DESIGN
Calculate Minimum Eccentricity
emin = 15 + 0.03 × 750
emin = 15 + 22.5 = 37.5 mm ≈ 38 mm
Even if the column is designed for purely axial load, codes require a minimum eccentricity to account for construction imperfections, material variations, and unforeseen moments. This ensures more realistic and safer design.
Calculate Design Moment
Md = 1150 × 38
Md = 43,700 kN·mm = 43.7 kNm
This is the minimum bending moment that must be considered in the design, calculated from the axial load and minimum eccentricity. The column must resist both this moment and the axial force simultaneously.
Calculate Normalized Parameters
ν = Nd / (b × h × fcd)
ν = 1,150,000 / (350 × 750 × 16.67)
ν = 1,150,000 / 4,375,875
ν = 0.263 ≈ 0.26
μ = Md / (b × h² × fcd)
μ = 43.7 × 10⁶ / (350 × 750² × 16.67)
μ = 43.7 × 10⁶ / 3,281,906,250
μ = 0.0133 ≈ 0.013
Determine Steel Coefficient from Charts
From interaction diagram: ψ ≈ 0.08
Note: Since the moment is very small (minimum moment condition),
we will likely need minimum steel reinforcement.
Calculate Required Steel Ratio
ρs = 0.08 × (16.67 / 365)
ρs = 0.08 × 0.0457
ρs = 0.00365 = 0.365%
ρmin = 1.0%
ρmax = 4.0%
ρs,calculated = 0.365% < ρmin = 1.0%
→ Use ρmin = 1.0%
Calculate Total Steel Area Required
Ast = 0.01 × 350 × 750
Ast = 2,625 mm²
Select Bar Size and Number
Area per bar = Ast / n = 2,625 / 8 = 328 mm²
Required diameter:
Ø = √(4A/π) = √(4 × 328 / π) = √(417.8) = 20.4 mm
Select: Ø22 mm (next standard size up)
Verification:
Area of Ø22 = π × 22²/4 = 380 mm²
Total provided = 8 × 380 = 3,040 mm²
3,040 mm² > 2,625 mm² ✓
Provided steel ratio: 3,040/(350×750) = 1.16% > 1.0% ✓
PART 2: SHEAR REINFORCEMENT DESIGN (TIES)
Check if Shear Reinforcement is Required
VRd = 0.22 × Asw × fcd
Where Asw is the area of shear reinforcement per unit length
For minimum shear capacity check:
Vd = 185 kN
Since we have shear force, we need to design ties.
Calculate Required Tie Area
d = h – d’ = 750 – 25 = 725 mm
Check concrete alone capacity:
Vcr = 0.65 × fctd × b × d × (1 + 0.07 × Nd/Ac)
Where fctd = 1.15 MPa (for C25)
Vcr = 0.65 × 1.15 × 350 × 725 × (1 + 0.07 × 1150×10³/(350×750))
Vcr = 0.65 × 1.15 × 350 × 725 × (1 + 0.07 × 4.38)
Vcr = 190,344 × 1.307
Vcr = 248,720 N = 248.7 kN
Since Vd = 185 kN < Vcr = 248.7 kN
→ Minimum shear reinforcement required
Design Minimum Ties
Asw = 2 × (π × 10²/4) = 2 × 78.5 = 157 mm²
For minimum reinforcement:
(Asw/s) ≥ 0.3 × (fctd/fywd) × b
Where fywd = 365 MPa, fctd = 1.15 MPa
(157/s) ≥ 0.3 × (1.15/365) × 350
(157/s) ≥ 0.330
s ≤ 157/0.330 = 475 mm
s ≤ b/2 = 350/2 = 175 mm
s ≤ 12Ømin = 12 × 22 = 264 mm (min. longitudinal bar)
s ≤ 200 mm (general limit for columns)
Governing: s ≤ 175 mm
Select: s = 150 mm (standard spacing)
(Two-leg stirrups at 150 mm spacing)
Final Design Summary
| Design Element | Requirement | Provided | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Column dimensions | 350 × 750 mm | 350 × 750 mm | ✓ |
| Axial load capacity | Nd = 1,150 kN | Adequate | ✓ |
| Moment capacity | Md = 43.7 kNm | Adequate | ✓ |
| Steel area required | 2,625 mm² | 3,040 mm² | ✓ |
| Steel ratio | ρmin = 1.0% | 1.16% | ✓ |
| Longitudinal bars | 8Ø22 | 8Ø22 | ✓ |
| Shear capacity | Vd = 185 kN | Vcr = 248.7 kN | ✓ |
| Ties/Stirrups | Min. required | Ø10 @ 150 mm | ✓ |
Design Verification Checklist
Longitudinal Reinforcement:
- Number of bars: 8 bars (adequate for rectangular column) ✓
- Bar diameter: Ø22 mm (standard size) ✓
- Steel ratio: 1.16% (between 1% and 4% limits) ✓
- Clear spacing: (350 – 2×25 – 4×22)/(3) = 71 mm > 25 mm ✓
- Bar distribution: 4 bars on each long face ✓
Transverse Reinforcement:
- Tie diameter: Ø10 mm (≥ Ø8 mm minimum) ✓
- Tie spacing: 150 mm (≤ 175 mm maximum) ✓
- Configuration: Closed rectangular ties ✓
- Number of legs: 2 (adequate for this width) ✓
Detailing Requirements:
- Concrete cover: 25 mm (adequate for indoor exposure) ✓
- Tie hooks: 135° hooks with 10Ø extensions ✓
- Corner bars: All corner positions have longitudinal bars ✓
Key Design Points
- Minimum moment condition: The column is designed for minimum eccentricity (38 mm) resulting in small moment (43.7 kNm)
- Axial load dominance: Normalized axial force ν = 0.26 indicates moderate compression
- Minimum steel controls: Calculated steel (0.365%) is less than code minimum (1.0%)
- Shear capacity: Concrete alone provides 248.7 kN > 185 kN required, but minimum ties still needed
- Tie spacing: Governed by b/2 = 175 mm; using 150 mm for better confinement
- Practical design: 8 bars provide symmetric arrangement and ease of construction
Construction Drawing Specification
COLUMN DIMENSIONS: 350 × 750 mm
LONGITUDINAL REINFORCEMENT: 8Ø22
TRANSVERSE REINFORCEMENT: Ø10 @ 150 mm c/c
CONCRETE GRADE: C25 (fck = 25 MPa)
STEEL GRADE: S420 (fyk = 420 MPa)
CONCRETE COVER: 25 mm
TIE HOOKS: 135° with 10Ø extension