ROOF TRUSS ANALYSIS
Complete Load Calculation and Support Reaction Analysis
PROBLEM STATEMENT
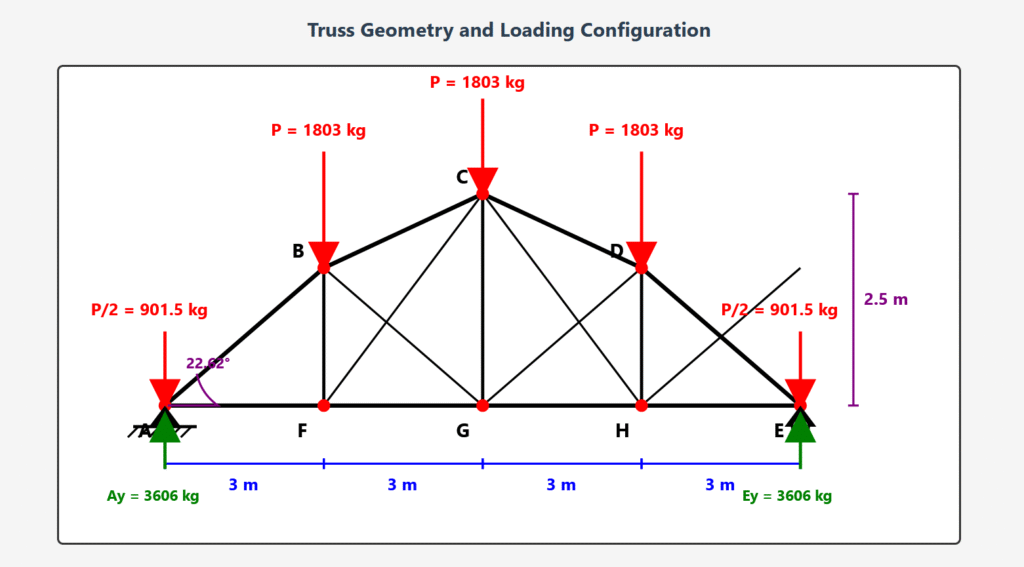
Calculate the joint loads and support reactions for a roof truss structure at the support points according to the given data:
- Altitude: 900 m above sea level
- Truss Spacing: 5.0 m
- Structure Self-Weight: 10 kg/m²
- Roof Covering Load: 12 kg/m²
- Total Span: 12 m (divided into 4 panels of 3 m each)
- Peak Height: 2.5 m above bottom chord
Truss Geometry and Loading Configuration
Given Data Summary
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Altitude | H | 900 m |
| Truss Spacing | – | 5.0 m |
| Structure Self-Weight | PMA | 10 kg/m² |
| Roof Covering Load | PÇÖ | 12 kg/m² |
| Panel Width | – | 3.0 m |
| Total Span | L | 12 m |
| Peak Height | CG | 2.5 m |
| Half Span | GE | 6.0 m |
SOLUTION – Complete Step by Step Analysis
Calculate Roof Slope Angle
tan(α) = CG / GE
tan(α) = 2.5 / 6.0
tan(α) = 0.4167
α = arctan(0.4167) = 22.62°
Calculate Sloped Length (CE)
CE² = CG² + GE²
CE² = 2.5² + 6.0²
CE² = 6.25 + 36
CE² = 42.25
CE = √42.25 = 6.5 m
Calculate Sloped Length per Panel (CD or DE)
CD = DE = CE / 2
CD = DE = 6.5 / 2
CD = DE = 3.25 m
Calculate Tributary Areas
S1 = Sloped length × Truss spacing
S1 = 3.25 × 5.0
S1 = 16.25 m²
S2 = Panel width × Truss spacing
S2 = 3.0 × 5.0
S2 = 15.0 m²
- S1 is used for loads applied perpendicular to the roof surface (roof covering, roofing materials)
- S2 is used for loads acting vertically downward (snow, self-weight of structure)
Calculate Snow Load (Pk)
Pk = 75 + 0.08(H – 1000) kg/m²
For H = 900 m (below 1000 m):
Pk = 75 + 0.08(900 – 1000)
Pk = 75 + 0.08(-100)
Pk = 75 – 8
Pk = 75 kg/m²
Calculate Total Snow Load at Joint (Wk)
Wk = Pk × S2
Wk = 75 × 15.0
Wk = 1,125 kg
Calculate Wind Load (PR)
PR = 150 × (sin α)²
PR = 150 × (sin 22.62°)²
PR = 150 × (0.3846)²
PR = 150 × 0.1479
PR = 22.19 kg/m²
Calculate Total Wind Load at Joint (WR)
WR = PR × S2
WR = 22.19 × 15.0
WR = 332.85 kg ≈ 333 kg
Calculate Roof Covering Load (WÇÖ)
WÇÖ = PÇÖ × S1
WÇÖ = 12 × 16.25
WÇÖ = 195 kg
Calculate Structure Self-Weight (WMA)
WMA = PMA × S2
WMA = 10 × 15.0
WMA = 150 kg
Calculate Total Load at Interior Joints
ΣP = Wk + WR + WÇÖ + WMA
ΣP = 1,125 + 333 + 195 + 150
ΣP = 1,803 kg
- Snow Load: 1,125 kg (62.4%)
- Wind Load: 333 kg (18.5%)
- Roof Covering: 195 kg (10.8%)
- Self-Weight: 150 kg (8.3%)
- Total: 1,803 kg (100%)
Calculate Total Applied Load on Structure
Total = (P/2 at A) + (P at B) + (P at C) + (P at D) + (P/2 at E)
Total = P/2 + P + P + P + P/2
Total = 4P
4P = 4 × 1,803
4P = 7,212 kg
Calculate Support Reactions Using Symmetry
Ay = Ey = Total Load / 2
Ay = Ey = 7,212 / 2
Ay = Ey = 3,606 kg
Ay + Ey – 4P = 0
3,606 + 3,606 – 7,212 = 0 ✓
The system is in equilibrium!
Verify Using Moment Equilibrium
Loads act at distances: 3m (B), 6m (C), 9m (D), 12m (E support)
ΣMA = -(1803×3) – (1803×6) – (1803×9) – (901.5×12) + 12Ey
0 = -5,409 – 10,818 – 16,227 – 10,818 + 12Ey
0 = -43,272 + 12Ey
12Ey = 43,272
Ey = 3,606 kg ✓
- Force equilibrium: ΣFy = 0 ✓
- Moment equilibrium: ΣMA = 0 ✓
- Reactions: Ay = Ey = 3,606 kg ✓
Complete Results Summary
| Description | Symbol | Calculated Value |
|---|---|---|
| Roof Slope Angle | α | 22.62° |
| Total Sloped Length | CE | 6.5 m |
| Panel Sloped Length | CD = DE | 3.25 m |
| Sloped Tributary Area | S1 | 16.25 m² |
| Horizontal Tributary Area | S2 | 15.0 m² |
| Snow Load Intensity | Pk | 75 kg/m² |
| Wind Load Intensity | PR | 22.19 kg/m² |
| Total Snow Load | Wk | 1,125 kg |
| Total Wind Load | WR | 333 kg |
| Total Roof Covering Load | WÇÖ | 195 kg |
| Total Self-Weight | WMA | 150 kg |
| Load at Interior Joints (B, C, D) | P | 1,803 kg |
| Load at Support Joints (A, E) | P/2 | 901.5 kg |
| Total Applied Load | 4P | 7,212 kg |
| Support Reaction at A | Ay | 3,606 kg |
| Support Reaction at E | Ey | 3,606 kg |
FINAL ANSWER
Joint Loads:
Interior Joints (B, C, D): P = 1,803 kg
Support Joints (A, E): P/2 = 901.5 kg
Support Reactions:
Ay = Ey = 3,606 kg
(Verified by both force and moment equilibrium)
Key Learning Points
- Geometric Analysis First: Always determine roof geometry (angle, sloped lengths) before load calculations
- Two Tributary Areas: Use sloped area for surface loads, horizontal area for vertical loads
- Altitude Effect: Snow loads decrease below 1000 m (by 0.08 kg/m² per meter) and increase above 1000 m
- Wind Load Formula: Proportional to sin²(α), meaning angle significantly affects wind pressure
- Load Superposition: Total load is the sum of all individual load components
- Half Loads at Supports: End joints receive half the load of interior joints due to tributary area
- Symmetry Advantage: Symmetric structures have equal reactions, simplifying analysis
- Equilibrium Verification: Always check both force and moment equilibrium to validate results
- These are unfactored service loads. Apply load factors (typically 1.2 for dead, 1.6 for live) for ultimate limit state design
- Analysis assumes loads applied only at joints (standard truss assumption)
- Multiple load combinations must be checked per design codes
- Wind and snow loads typically don’t act simultaneously at full values – check code requirements
- Actual member forces in truss bars require method of joints or method of sections analysis